Red Hat Insights¶
- Version:
3.0
- Date:
Apr 19, 2024
Introduction¶
The Red Hat Insights application is built upon four somewhat independent subsystems:
the collection component;
the processing engine component;
the plugin components; and
the customer interface component.
The collection component is called Red Hat Insights Client (“Client”) and is part of the Red Hat Enterprise Linux distribution. It is installed via RPM onto a host system where it collects information to send to the infrastructure engine for analysis. The processing engine component is called Insights Core (“Engine”) and runs on Red Hat internal systems to process the information collected by the Client and provides results to the customer interface component. The Engine processes the information by extracting each unique set of data, parsing the data into facts, and analyzing the facts via algorithms. Parsing and analysis of the information is performed in a collection of plugin components. The parsing and combining is performed by the Parser and Combiner plugins, and the analysis is performed by Rule plugins (collectively “Plugins”). The results of the analysis are presented to the user via the user interface component (“UI”). The figure below provides a graphical overview of the components and the information flow.
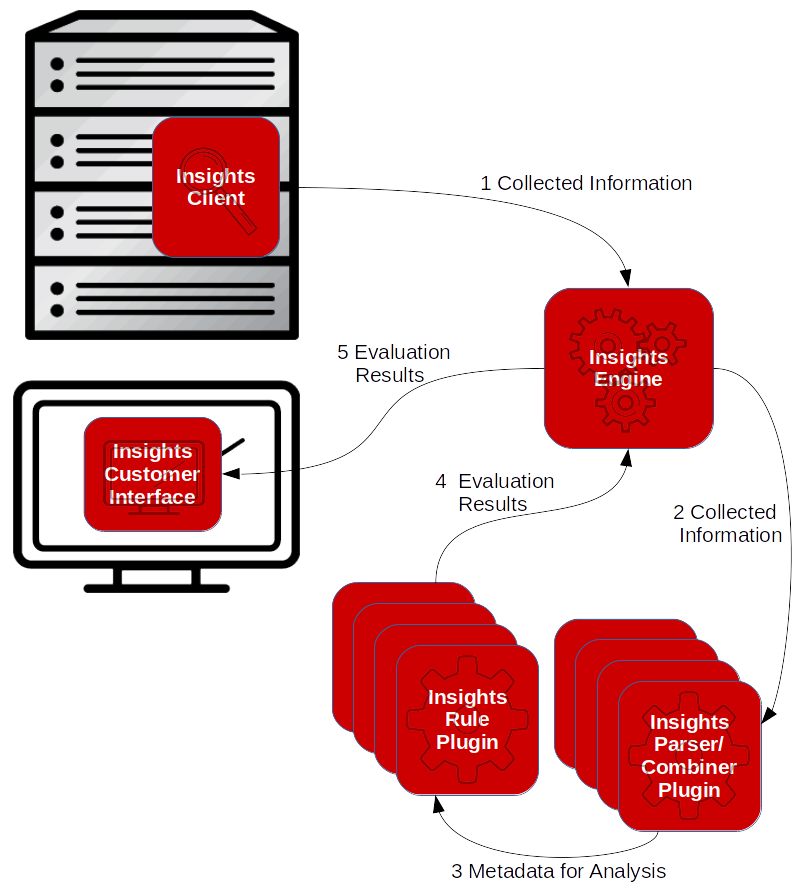
Overview of the Insights Components and Information Flow
Insights Client - Collection¶
Collection of information is performed by the Client component of Red Hat Insights. The Client RPM is installed on one or more host systems where data collection is to be performed. A host system may be a physical system or a virtual machine. Information collected by the Client is filtered to remove sensitive information and then sent to the Engine for analysis. Collection is typically performed daily but may be configured to run on other schedules. It may also be disabled/enabled by the system administrator.
More information about the Client component can be found at Red Hat Insights Portal and source code is available on the Red Hat Insights Client GitHub Project.
Red Hat Insights Core - Data Analysis Engine¶
Once host information has been collected by the Client it is transferred to the Engine for processing. The Engine is a SaaS application hosted at Red Hat. The Engine processes information as it is received and provides the results to the Customer Interface for review by the customer.
The Engine begins processing by unarchiving the information and identifying each type of information that included in the Client upload. The Engine then configures the Plugins into a map/reduce network and executes them to analyze the data. The workflow consists of the steps:
parsing the data into facts specific to the system (such as RPMS installed, CPU details, storage details, etc.);
combining certain facts where there are multiple sources, or differences across platforms (this provides a more consistent set of facts for the analysis step); and
analyzing the facts to determine the results.
Each Plugin provides results which are all collected by the Engine and upon job completion the results are made available to the Customer Interface for review. The Engine evaluates the input data and only invokes Plugins that are necessary to process the data that is present. The Engine also optimizes the Rules so that they are only invoked in the workflow if the necessary facts are present.
More information about the Red Hat Insights Core component can be found on Red Hat Insights Core GitHub Project.
Plugin Components - Parsing and Fact Analysis¶
The Engine coordinates analysis of the information via the Plugins. There are three types of plugins that are used in the analysis workflow, Parsers, Combiners, and Rules. Parsers parser data into facts. Combiners aggregate facts into higher level facts. Rules analyze facts.
Parser Plugins¶
Parser plugins are responsible for analyzing the raw data
and converting it into usable facts that can be evaluated by the
Combiners and Rules. Each Parser plugin is typically responsible
for parsing a specific set of data. For instance, the Mount parser
plugin (insights.parsers.mount.Mount)
parses the output of the mount command and the FSTab
parser plugin (insights.parsers.fstab.FSTab)
parses the contents of the /etc/fstab/ file.
Combiner Plugins¶
Combiner plugins perform aggregation of facts to make the facts more consistent
to Rules. For instance the Red Hat Enterprise Linux release number (i.e. 6.8 or 7.3)
is available
in the file /etc/redhat_release and may also be derived from the command
uname -a. The redhat_release Combiner plugin
(insights.combiners.redhat_release()) looks at the facts from
both Parsers (insights.parsers.redhat_release.RedhatRelease and
insights.parsers.uname.Uname) to determine the major and minor release
numbers. The Combiner will use the best source of information first, and then
use the second source if the first is not available. This allows Rules to
simply rely on this Combiner as the source of the fact instead of having
to look at the facts from two different Parsers.
Rule Plugins¶
Rule plugins perform the analysis of the facts made available by the Parsers and Combiners. Rules may look at any number of facts to determine if a symptom or condition is present in a system, or that one is likely to occur in the future. For instance if particular ssh vulnerability is present when using Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.1 with a particular setting in file /etc/ssh/sshd_config, a Rule could look at the facts from the Red Hat Release Combiner to determine if the system was running 7.1 and then check facts from the sshd_config file to determine if the setting was present. If both facts are true then the Rule will report the results and it will be displayed with information regarding the vulnerability and how it can be resolved on the specific system. These results from all Rules are accumulated and consolidated by the Engine to provide to the Customer Interface.
Customer Interface - Analysis Results¶
The Customer Interface provides views of the Insights results via the Red Hat Customer Portal. Multiple views are provided for all of customer’s systems reporting to Insights. Information is provide regarding the results including metadata related to the findings, an explanation of the findings, and information related to correction of identified conditions and/or problems. The Customer Interface provides many customization options to optimize each customer’s specific needs.